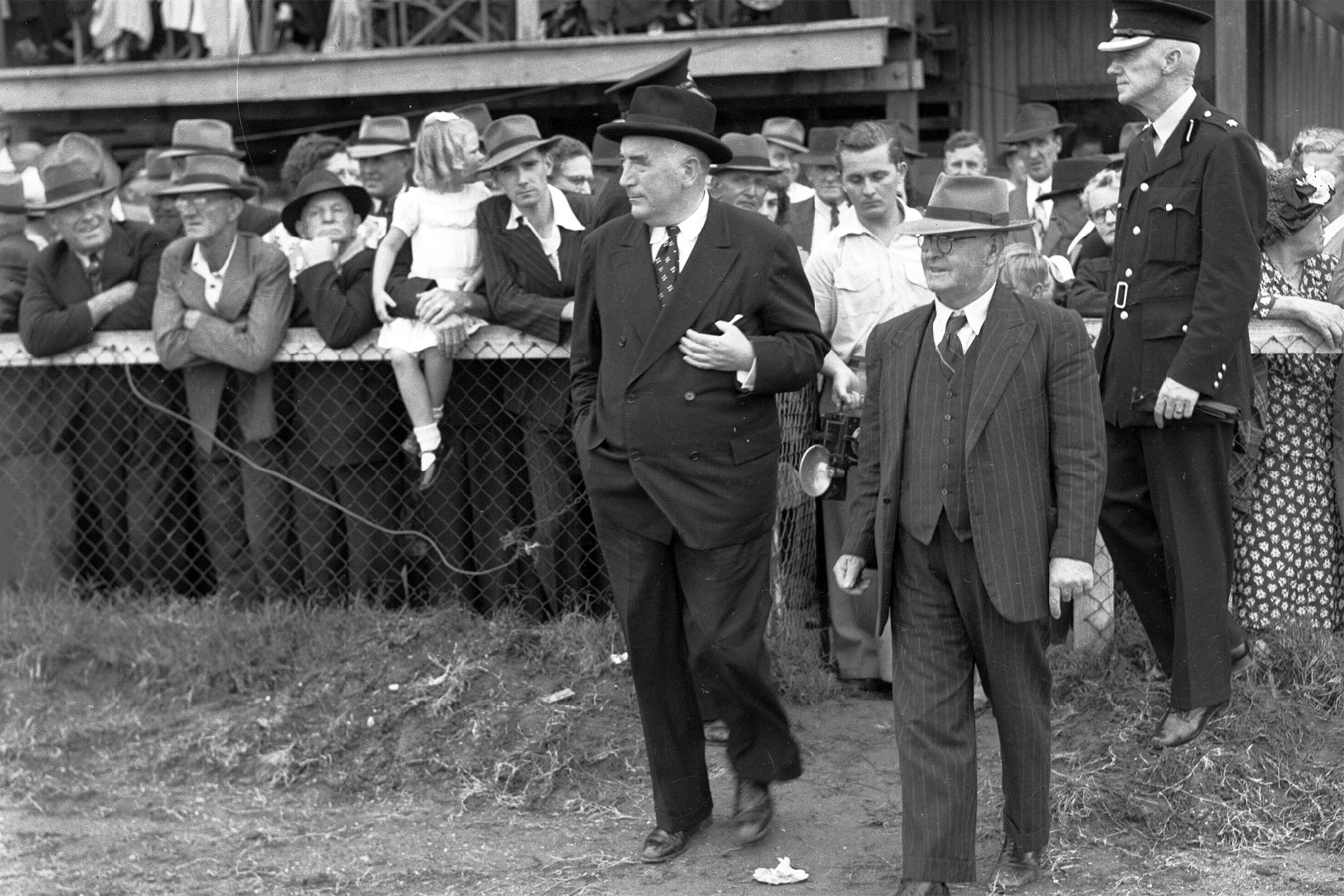
More than most prime ministers, though befitting his longevity, Robert Gordon Menzies has been the subject of a significant number of books, articles and commentary — including his own memoirs, political tracts and broadcasts made during and after his political career. For interested researchers, Menzies’s papers and recorded interviews and the many books in his own library are all housed at the Robert Menzies Institute at Melbourne University.
The sheer volume of material continues to fuel efforts to document and analyse the career of Australia’s longest-serving prime minister. The latest is a multi-author, multi-volume (four are promised) appraisal edited by the Menzies Institute’s Zachary Gorman. Based on a series of conferences, the books aim to promote “discussion, critical analysis and reflection on Menzies, the era he defined and his enduring legacy.” Contributions are not limited to those of unabashed admirers; writers from the other side of the political fence also offer their assessments, as do ostensible neutrals.
The first volume, The Young Menzies: Success, Failure, Resilience 1894–1942, covers the period from Menzies’s birth in 1894 to 1942, though not all chapters fit neatly within those boundaries. James Edelman and Angela Kittikhoun’s useful chapter on Menzies and the law, for example, takes in the Communist Party Dissolution Bill, eight years beyond 1942.
Following political scientist (and ex-MP) David Kemp’s introduction, the book’s early chapters focus on the family environment into which Menzies was born and the social and political culture of the era. As most readers will be aware, his father ran a general store in the western Victorian town of Jeparit, saving the son from any credible charges of having been born with a silver spoon in his mouth. But while the small business ethos had a crucial impact on Menzies’s political philosophy, he was exposed to a different worldview by his maternal grandfather, John Sampson, an active trade unionist, though without being persuaded to change his own emerging outlook.
Menzies’s academic record in Melbourne University’s law faculty was outstanding and he also took part in student politics and campus journalism. His failure to enlist during the first world war — a family decision prompted by the fact that two brothers were already serving — is well known, and journalist Troy Bramston reveals how it may have contributed to Menzies’s fiancée’s ultimate decision to break off their engagement. Menzies had no doubt that his failure to enlist propelled him away from a brilliant legal career and onto the parliamentary path. He needed to offer “public service.”
For this reviewer, one of the most interesting chapters is historian Greg Melluish’s account of Menzies’s advocacy of liberal education and its connection with his ideas about democracy. That Menzies was a “scholarship boy” at both school and university is reasonably well known and, Melluish argues, helps explain his support for “meritocracy” rather than inherited and entrenched privilege (with an obvious exemption for the monarchy). This commitment seems crucial in explaining Menzies’s insistence that he (and later, his party) was liberal, not conservative.
Of course, conservatism existed (and exists) in Australia, and the parties Menzies joined and led garnered the vast preponderance of that vote. He revered English political and legal institutions as springing from liberal values, but their defence surely entailed a conservative outlook. Melluish stresses that Menzies understood English democracy as reflective of a specific common culture; in contrast to the Americans, “he did not see democracy as being universally applicable.” This could help explain why conservatives may view multiculturalism as a problem, undermining the necessary foundations of their version of democracy — a question that will perhaps be tackled in later volumes. Of course, Menzies’s view could also lend itself to the darker idea that democracy is not suitable for all, especially those viewed as “backward.”
Among other prime ministers, probably only Gough Whitlam could be as closely identified with the case for liberal education. For Menzies, writing in the 1930s, British history demonstrated that such an education “would produce the sorts of people who possessed the capacities to make that system of government [Westminster] work properly.” Ironically, in view of today’s emphasis on utilitarian degrees, Menzies can be seen as enlisting the (now) maligned bachelor of arts in defence of the practical aim of good government.
Melluish also usefully distinguishes between Menzies’s idea of a liberal education and the wider idea of “Western civilisation.” Menzies was fixated on Australia’s British heritage; the Greek and Roman stuff could, it seems, be left to people like Whitlam.
Menzies’s version of the university was obviously not the “oppositional” one. But, as Melluish points out, this critical variant was emerging at the time Menzies was writing. It would probably approach its zenith during the second half of Menzies’s long term in office — which should make for an interesting discussion in the final volume in this series.
Political scientist Judith Brett explores the parallels between Menzies and Alfred Deakin, sons of small businessmen, both of them influenced by the liberalism of the Victorian goldfields, both following very similar educational paths, and of course, both having more than one go as prime minister. It is Deakin, she writes, “whom Menzies might have looked to as an exemplar of national leadership.”
A useful reminder of the important role religion could play in forming political beliefs comes in historian David Furse-Roberts’s chapter on the impact of Menzies’s Presbyterianism. The connection between his faith and his political philosophy seems so strong that a liberal atheist might have felt less than welcome in the party Menzies would form. And, had he been around, Menzies may well have been puzzled to observe some Liberal staffers take an affirmation rather than an oath when they appeared in the defamation case brought by Bruce Lehrmann against Network Ten and one of its journalists.
By contrast, it would be an oddity today if any senior politician identified mainstream religion (as opposed to the “prosperity gospel” variant embraced by some prominent conservatives) as a key factor in their political outlook. As judged by Furse-Roberts, Menzies’s version of Presbyterianism emphasised a “selfless individualism,” acknowledging the ameliorative role of the state but also its limitations: “it fell primarily to the compassionate spirit and self-sacrifice of individuals to succour the needy and further the common good.” This clearly eschews socialism, but Furse-Roberts suggests it goes “far beyond John Stuart Mill’s minimalist ethic of ‘no harm’ to others.” One might observe how that reference to the “common good” contrasts with the overwhelmingly individualist emphasis of the more recent version of the Liberal Party.
Historian Frank Bongiorno’s chapter, “Menzies and Curtin at War,” is a finely balanced contribution, acknowledging the positives of Menzies’s first prime ministership and also (in anticipation) recognising his “postwar nation-building achievements,” which “look better every year, as we contemplate the policy failures of our own century and the conspicuous absence of compelling vision.” This generosity from a Labor-leaning historian suggests that the defensiveness of Liberal partisans in certain chapters may to some extent have been directed at a shrinking target.
Anne Henderson mounts a characteristically robust defence of Menzies from charges of appeasement and softness on Nazi Germany, stressing the absence of a perfect record among any of the key players. Mindful of the passage of time, I was left wondering how many Australians would know to whom “Pig-Iron Bob” refers. How many in the press gallery?
Journalist Nick Cater examines the role of Menzies’s famous “The Forgotten People” radio address in 1942, highlighting the importance of the family home as the central focus of that talk. While a Labor minister could deride this support for increased home ownership as turning workers into “little capitalists,” Menzies’s philosophy emphasised the “social, economic and moral value of home ownership.” Saving for a home was a “concrete expression of the habits of frugality and saving.” National patriotism, in other words, “inevitably springs from the instinct to defend and preserve our own homes.” How might the renters on the battlefields in 1942 have responded to this observation, I wonder?
Political scientist Scott Prasser sums up the learning experiences that would enable Menzies to resurrect his career and become Australia’s longest-serving prime minister. This involves some projection, for he still had much learning to do (during seven more years as opposition leader) after the notional end date for this volume. That quibble aside, Prasser’s contribution is a useful one since Menzies’s success can’t be attributed mostly to luck and dud opponents. The checklist: modest promises, sound coalition relations, a willingness to adopt new directions, and an awareness of the nation’s political architecture. His return to power and the use to which he put his learning experiences await us in the next volume.
In his introduction to the second and latest of the series, The Menzies Watershed, editor Zachary Gorman acknowledges the limitations of the “call for conference papers” method the project employs, which risks missing “certain topics of great interest and relevance.” This dilemma is reflected in the ensuing chapters, with some likely to be of appeal to the general political scholar–aficionado and others more in the niche category. My focus will be largely on the former.
In his chapter on Menzies and the Movement, Lucas McLennan makes the case for a good deal of similarity of emphasis between Menzies’s Anglo-Protestantism and the version of Catholic social teaching (and consequent public policy) embraced by lawyer–activist B.A. Santamaria and his disciples in the (Catholic Social Studies) Movement. It is certainly the case that both men would have seen their vigorous anti-communism as having a strong religious component, especially reflected in the anti-communist foreign and defence policies embraced by Menzies’s party and endorsed by Santamaria and (after the Labor Party’s split in 1955) his political creation the Democratic Labor Party.
McLennan’s case is possibly less convincing on the domestic front. While the Movement may have preferred subsidiarity over centralism, it seems unlikely that Menzies would have seen much merit in the (frankly weird) land settlement proposals advanced by Santamaria. And we can be fairly confident that the Movement’s view (as expressed in 1948) that Christians should seek “to break up concentration of wealth” would not have secured much support at a meeting of the Kooyong branch of the Liberal Party. Ultimately, even Santamaria’s version of Catholic social teaching necessarily involved an element of collectivism that would not have appealed to Menzies.
Anne Henderson’s brief chapter on Menzies’s successful opposition to Labor’s bank nationalisation plans possibly tells the reader as much about the Chifley government’s ideological rigidity (or commitment to principle — take your pick) and misreading of the public mood as it does about Menzies’s deft exploitation of the issue. Two decades after the Depression, the anti-banks sentiment was clearly not what it used to be, although Henderson’s depiction of the banks battle as “class war as Australia had never seen it” might have been challenged by some survivors from that period. In passing, it might be observed that since Labor lost the double dissolution election it provoked on this issue in 1951, it has not held a Senate majority on any occasion.
Tom Switzer evidences and reinforces the generally accepted wisdom that Menzies was no radical right-wing reformer. He retained and relied on several of the senior bureaucrats who had advised Chifley, and his economic policies were of the Keynesian variety, reflecting a consensus that would persist until the end of the Fraser period. In his introduction to this volume, Gorman had noted Menzies’s good fortune in not being “exposed to a centre-right echo chamber of policy advice,” insulating him from big overreaches (with the exception of the attempt to ban the Communist Party).
Keynesianism is again a key theme in David Lee’s chapter on economic management. It also contains a useful outline of cabinet and public service structures and processes in the early years of the Menzies government.
Troy Bramston’s chapter, “The Art of Power,” draws on his well-received biography of Menzies and hence comment here will be minimal: Menzies had been an effective political campaigner, “but campaigning is not government” (wise advice). Building on his previous experience, consultation, reflection and wide reading, he developed a capacity for management and administration that served him well.
Charles Richardson examines aspects of Menzies’s approach to the crown and imperial relations, the Statute of Westminster and the office of governor-general, drawing some comparisons with the attitudes of his nemesis H.V. Evatt. In referring to Menzies’s concern about the “separate status of the crown in right of the different dominions”— the question of how the monarch could be at peace and war at the same time in relation to the same foreign power — Richardson delightfully describes this as an “absurdity” that we still live with. The fact that most wars are now waged without formal declarations of war may help, at least at a technical level.
Richardson endorses the view that Menzies should have made the switch from a British to an Australian governor-general before Casey’s appointment in 1965, but notes the prime minister’s quaint criterion that it was essential with any appointment that “the Queen knew them.”
Lyndon Megarrity seeks to correct the misconception that Australia’s involvement with overseas students only commenced with the Colombo Plan. He outlines the history of such activity (which could involve some fancy manoeuvring round the White Australia policy) and describes policy before the second world war as “ad hoc and reactive.” The Chifley government entered the soft diplomacy business of scholarships, but Megarrity sees any potential benefits as being negated by immigration minister Arthur Calwell’s notorious hardline attitude on deportations: no grey areas in the White Australia policy for him.
The role of the new external affairs minister Percy Spender in the creation of the Colombo Plan in 1950 is well known. While acknowledging the Chifley government’s creation (pre-Colombo) of a relevant policy management framework, Megarrity credits the Menzies government with a defter handling than Labor of tensions between the Plan and the White Australia policy, assisting with the overall enhancement of Australia’s reputation in the region. In the cold war context, the scheme could “help maintain stability in Southeast Asia and increase resistance to Communism.”
Chapters on the creation of the Australian Secret Intelligence Service and on the role of Spender in (among other things) negotiating the ANZUS treaty serve to highlight the electoral supremacy the Menzies government would establish as the guardian of national security, an advantage his party has largely retained to the present day. Nicolle Flint revisits the issue (it probably no longer qualifies as a “debate”) over whether Menzies’s role in the Liberal Party’s creation has been overstated (spoiler alert: no). Lorraine Finlay, addressing the dilemma of “what liberty should be provided for the enemies of liberty,” focuses on the attempts to ban the Communist Party, though current trends may remind us of the timelessness of that dilemma. Andrew Blyth provides an account of think tanks’ influence on the Menzies government, but to some extent the title is misleading: the Institute of Public Affairs was effectively the only player in that game, although pressure groups and committees of inquiry are also covered in the chapter.
Christopher Beer’s chapter uses the federal electorate of Robertson on the central New South Wales coast to make some observations about the impact of early Menzies government policies. He includes useful electoral information about the seat, which serves (for this reviewer) to highlight the absence of comparable nationwide electoral data and commentary on the elections of the period. Clearly, the “call for papers” did not evince the relevant interest.
By the end of the period covered in this volume, Menzies had won three elections as Liberal leader, disarming his internal critics, and even greater dominance lay ahead: Labor partisans might like to look away now. •
The Young Menzies: Success, Failure, Resilience 1894–1942
Edited by Zachary Gorman | Melbourne University Publishing | $44.99 | 222 pages
The Menzies Watershed: Liberalism, Anti-Communism, Continuities 1943–1954
Edited by Zachary Gorman | Melbourne University Press | $45 | 256 pages