One of the arguments deployed to dismiss global warming and the uniqueness of the long, gruelling fire season of 2019–20 was that Australia has always had bushfires. Bushfire is indeed integral to our ecology, culture and identity; it is scripted into the deep biological and human history of the fire continent. But some politicians and media commentators used history lazily to deny that anything extraordinary is happening and drew on the history of the Victorian firestorm as if it represented national experience.
We need to bring some historical discrimination to debates about what was new about the Black Summer. In particular we need to look at the history of firestorms, the distinctive fatal fires of southeastern Australia that culminated in named days of terror: Black Thursday 1851, Red Tuesday 1898, Black Sunday 1926, Black Friday 1939, Black Tuesday 1967, Ash Wednesday 1983 and Black Saturday 2009. How did the summer of 2019–20 relate to this grim lineage?
Black Thursday, 1851
The British colonists of Australia came to “this continent of smoke” from a green, wet land where fire was cosseted and coddled. They had rarely, if ever, seen free-ranging fire at home for it had been suppressed and domesticated over generations. They had so tamed fire that they had literally internalised it in the “internal combustion” of the steam engine.
These representatives of the industrial revolution brought to Australia many new sources of ignition, yet they also introduced houses, cattle, sheep, fences and all kinds of material belongings that made them fear wild fire. And they found themselves in a land that nature and human culture had sculpted with fire over millennia, a land hungry for fire and widowed of its stewards by the European invasion. It was an explosive combination. They did not know what the bush could do.
The foundational firestorm of Australian settler history occurred a few months after the residents of the Port Phillip District heard the news that British approval had been given for their “separation” from New South Wales. The impending creation of a distinct colony, soon to be called Victoria, was a cause for much celebration in Melbourne in November 1850, and a five-day holiday was declared.
Three months later, on Thursday the sixth of February 1851, in the soaring heat of a scorching summer, terrifying fires swept across the forests, woodlands and farms of the southeast. “Separation” had been celebrated with hilltop bonfires and now it was sealed by a scarifying firestorm. It was right that fire should forge the political identity of the most dangerous fire region on the planet.
“Black Thursday,” wrote the visiting British writer William Howitt, who arrived the year after the fire, “is one of the most remarkable days in the annals of Australia.” “The whole country, for a time, was a furious furnace,” he reported, “and, what was the most singular, the greatest part of the mischief was done in one single day.” He then went on to make some startling parallels. “It is a day as frequently referred to by the people in this colony as that of the Revolution of 1688 in England, of the first Revolution in France, or of the establishment of Independence in the United States of America.” In Australia, Howitt seemed to be suggesting, it was nature more than politics that would shape our identity.
Black Thursday, “the Great Bush Fire,” was a revolution of a kind. It was the first of the Black Days to be named by Europeans, the first recorded firestorm to shock and humble the colonists. Although the newcomers had quickly learned to expect bushfires, this was something else; its magnitude and ferocity terrified all who experienced and survived it.
At first the Melbourne Argus could hardly credit the reports from the bush, but then the breathless testimony kept tumbling in. Drought, high temperatures and ferocious northerly winds fanned the flames into a giant conflagration. People rushed to fight with green boughs “as in ordinary bushfires,” but all were forced to flee. Flames leaped from tree to tree like lightning; the fire careered “at the rate of a horse at full gallop”; sheep, cattle, horses, kangaroos and smaller native animals hurtled before it and hosts of birds were swept up in it: “the destruction of the wild creatures of the woods, which were roasted alive in their holes and haunts, was something fearful to contemplate.” People “went to bed, or lay down (for many did not dare go to bed), in a state of the greatest suspense and doubt as to whether they should see daylight next morning.”
Four days after the fire, Frances Perry, wife of the Bishop of Melbourne, recorded that “in some parts of the country the people are completely panic-struck. They thought, and well they might, that the world was coming to an end.”
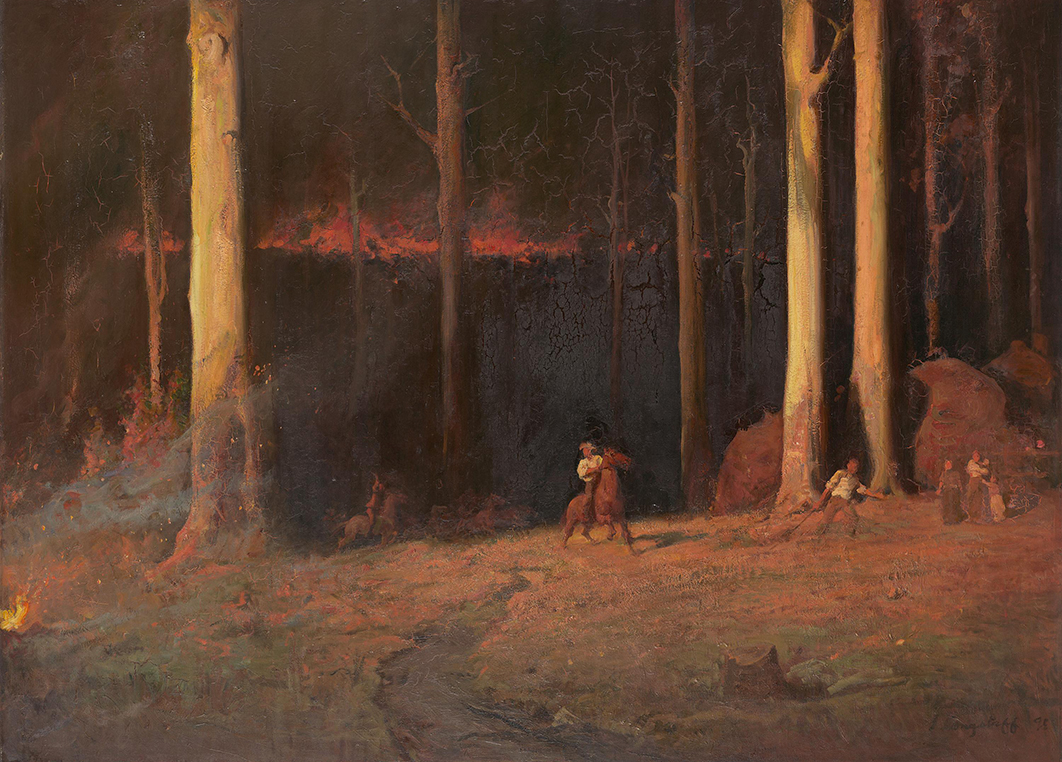
The words of survivors painted a picture strikingly similar to the grand panorama of Black Thursday (1864) by artist William Strutt. For his imagery he drew on reportage as well as his own experience of the heat, smoke and fear of the day. Over three metres in breadth, the painting depicts what Strutt called “a stampede for life,” where people and animals, eyes wild with panic, flee southwards in terror.

Stampede for life: William Strutt’s Black Thursday, February 6th 1851 (1864). Click here to enlarge. State Library of Victoria
The “Great Bush Fire” of 1851 was the first large-scale firestorm to terrorise the British colonists. It wreaked its havoc just a decade and a half after British pastoralists invaded the Port Phillip District of New South Wales. Sheep, cattle and people had swiftly moved into the grasslands of the southeastern corner of the continent, but in 1851 the invaders had only recently outnumbered Aboriginal peoples and Indigenous burning regimes persisted in some places.
Because of its timing on the cusp of this change, Black Thursday was an intriguing amalgam of old and new Australia. It was an event embedded in the unravelling ecological and cultural rhythms of the southeastern corner of the continent. But Black Thursday was also an outrageous outbreak of disorder, the first schism in the new antipodean fire regime, a portent of things to come.
Red Tuesday, 1898
European settlers feared and suppressed fire near their properties and towns, and misjudged its power in the bush. But it did not take them long to begin to use fire for their own purposes, even if clumsily and dangerously. “The whole Australian race,” declared one bushman, has “a weakness for burning.” The language the bush workers used — “burning to clean up the country” — was uncannily like that of Aboriginal peoples.
In the drier forests of the ranges (but generally not the wet mountain ash forests, which had less grass), graziers used fire as Aboriginal peoples had done: to keep the forest open, to clean up the scrub, to encourage a “green pick,” and to protect themselves and their stock from dangerous bushfire. But, unlike Aboriginal peoples, the newcomers were prepared to burn in any season. And the legislative imperative for settlers was to “improve” the land they had colonised — and “improvement” first meant clearing. The Australian settler or “pioneer” was a heroic figure depicted as battling the land and especially the trees.
This fight with the forest assumed theatrical dimensions in South Gippsland, where each summer neighbours gathered to watch the giant burns that, they hoped, would turn last year’s fallen and ring-barked forest into this year’s clearing. They needed to establish pastures as quickly and cheaply as possible. Small trees were chopped, undergrowth was slashed, and sometimes large trees were felled so as to demolish smaller timber that had previously been “nicked,” thereby creating, as one settler put it, “a vast, crashing, smashing, splintering, roaring and thundering avalanche of falling timber!” The slashed forest was left to dry until the weather was hot enough for the annual burn, the frightening climax of the pioneer’s year.
In the mostly wet sclerophyll forest of the South Gippsland ranges, some of it mountain ash, it was often hard to get a “good burn” because of the heavy rainfall and the thick scrub’s resistance to wind. Farmers therefore chose the hottest summer days for these burns, “the windier and hotter the day the better for our purpose.” These settlers of the world’s most fire-prone forests awaited the most fatal days.
A “good burn” could so easily become a firestorm and in Gippsland in 1898 it did. “Red Tuesday” (1 February) was the most terrifying day of the “Great Fires” that year, a whole summer of fear and peril. Intense clearing fires had accompanied ringbarking, ploughing, sowing and road-making in Gippsland for two decades, but settlers were still shocked by the Great Fires, which were like nothing they had ever experienced. Although they were stunned by the speed and violence of the firestorm, the new farmers understood that it was a product of their mode of settlement. Their principal pioneering weapon had run amok. As farmers burned their clearings into the encircling edges of the wet, green forest, they might have guessed that soon the fires would link up and overwhelm them.
Just as Black Thursday was memorialised in a great painting so was Red Tuesday captured in a grand work of art. When historian Stephen Pyne surveyed fire art around the world, he found Australian paintings to be exceptional for their gravitas, their capacity to speak to cultural identity or moral drama. “Bushfires did not simply illuminate the landscape like a bonfire or a corroboree,” he wrote, “they were the landscape.”
This is vividly true of John Longstaff’s depiction of Gippsland, Sunday Night, February 20th, 1898. Longstaff was born on the Victorian goldfields a decade after Black Thursday and travelled to Warragul to witness the long tail of the 1898 fires. Whereas Strutt’s painting was intimate in its terror and chaos, showing us the whites of the eyes of people and animals, Longstaff evoked the drama through its magisterial setting. Human figures are dwarfed by towering mountain ash trees and the immensity of the bush at night, and appear encircled and illuminated by fire. Flames lick at the edge of the clearing and a leaping firestorm races towards us from a high, distant horizon.
Longstaff exhibited his grand painting in his Melbourne studio in August of that year, lit by a flickering row of kerosene-lamp footlights. Gippsland, Sunday night, February 20th, 1898 is a painting of a landscape, and it focuses on the forest as much as the fire and the settlers. “The Great Scrub,” the enemy of the settlers, is a powerful presence in the panorama; it inspires as much awe as the flames. The people in the painting, who are seeking to “settle” this fearful forest, are enclosed and entrapped by its vast darkness. The erupting bushfire is both a threat and a promise.
Burning off
Firestorms became more frequent in the twentieth century, as sawmilling and settlement moved more deeply into the mountain forests of Victoria. The greatest of them came on Friday 13 January 1939, the grim climax of a week of horror and a summer of fire across New South Wales, South Australia, the Australian Capital Territory and Victoria. In that week, 1.4 million hectares of Victoria burned, whole settlements were incinerated, and seventy-one people died. Sixty-nine timber mills were engulfed, “steel girders and machinery were twisted by heat as if they had been of fine wire,” and the whole state seemed to be alight.
Judge Leonard Stretton, who presided over the royal commission into the causes of the fires, pitied the innocence of the bush workers, immigrants in a land whose natural rhythms they did not yet understand:
Men who had lived their lives in the bush went their ways in the shadow of dread expectancy. But though they felt the imminence of danger they could not tell that it was to be far greater than they could imagine. They had not lived long enough. The experience of the past could not guide them to an understanding of what might, and did, happen.
Stretton investigated the settlers’ culture of burning, taking his commission to bush townships and holding hearings in temperatures over 100°F (38°C). His shocking finding was that “These fires were lit by the hand of man.” Yet rarely were they malevolent arsonists. Mostly they were farmers and bush workers, and their fire lighting was casual and selfish, sometimes systematic and sensible, and increasingly clandestine and rebellious. They were settlers burning to clear land and graziers firing the forest floor to promote new grass. Burning was a rite — and a right. They were landowners who, when they saw smoke on the horizon, threw a match into their home paddock.
Settlers felt “burning off” helped to keep them and their neighbours safe. Travellers to the Yarra Valley in the first decades of the twentieth century wouldn’t have been surprised to see “half a dozen fires on the sides of mountains.”
When the Forests Commission of Victoria was founded in 1918, it assumed control of the state forests and forced graziers out if they did not stop burning their leases. Forest officers, charged with conservation of timber, tried to suppress fire, but farmers and graziers believed that their burning kept the forest safe from fire by keeping fuel loads down. George Purvis, a storekeeper and grazier at Moe in Gippsland, explained to the 1939 royal commission that everybody used to burn off many years ago: “We could meet a few of our neighbours and say ‘What about a fire’… Nowadays, if we want a fire we nick out in the dark, light it, and let it go. We are afraid to tell even our next door neighbour because the Forests Commission is so definitely opposed to fires anywhere, that we are afraid to admit that we have anything to do with them.”
As a result, Purvis explained, the bulk of farmers did not burn their land as much as they wished. And so, as fires gathered force in the week before Black Friday, people desperately burned to save their property and their lives. It was considered better to burn late than never, and these fires (indeed “lit by the hand of man”) “went back into the forest where they all met in one huge fire.”
Perhaps fire was so much a part of the Australian landscape and character that it could never be eliminated or suppressed. It had to be accepted and used, and perhaps it could be controlled. The 1939 royal commission signalled a new direction. In his recommendations, Stretton gave official recognition to a folk reality and tried to give focus and discipline to the widespread popular practice of burning to keep the forest safe. He recommended that the best protection against fire was regular light burning of undergrowth at times other than summer. Only fire could beat fire.

Vivid word-picture: the report of the 1939 royal commission.
As Stephen Pyne observed, this “Australian strategy” was in defiant counterpoise to the North American model of total fire suppression. The strategy was reinforced by another royal commission, this one following the 1961 Dwellingup fires in Western Australia, which endorsed systematic, expansive, hazard-reduction burning of the jarrah forests of the southwest.
It took time for official “controlled burning” to supplant unofficial “burning off.” In 1967, a Tasmanian firestorm provided dramatic evidence of the persistence of rural traditions of burning. On 7 February, which became known as Black Tuesday, a “fire hurricane” stormed through bushland and invaded Hobart’s suburbs, coming within two kilometres of the CBD. The fire caused the largest loss of life and property on any single day in Australia to that time.
Black Tuesday had strong elements of Black Friday 1939 embedded within it. Of the 110 fires burning on that Tuesday, ninety started prior to the day and seventy were uncontrolled on the morning of the 7th. Significantly, only twenty-two of the 110 fires were started accidentally; eighty-eight were deliberately lit. In other words, bushfires were common, deliberate and allowed to burn unchecked. “No one worried about them too much,” reflected Tasmanian fire officer John Gledhill, echoing Stretton.
Tasmania’s 1967 Black Tuesday fire, with its heart in the expanding suburbs of Hobart, signalled a new type of firestorm in Australian history. The bush had come to town. But the town had also come to the bush, insinuating its commuters and their homes among the gums. This event initiated an era of fires that would invade the growing urban interface with the bush: Ash Wednesday 1983 (Adelaide and Melbourne); Sydney 1994; Canberra 2003, when more than 500 suburban homes were destroyed in the nation’s capital; and Black Saturday 2009, when only a wind change prevented the Kilmore East fire from ploughing into Melbourne’s densely populated eastern suburbs.
During the second half of the twentieth century, casual rural fire lighting gradually became criminalised. The law was enforced more strongly and public acceptance of open flame declined. Fire was gradually eliminated from normal daily experience as electricity took over from candles, kerosene and, eventually, even wood stoves. Firewood for the home became more recreational. “Smoke nights” — once part of the fabric of social life and an especially masculine ritual — went into decline as smoking itself became a health issue. Instead of being a social accompaniment and enhancement, smoking was pushed to the margins of social life, even becoming antisocial.
It had been different in the interwar years: in 1939 the Red Cross, “concerned about the health of the bush fire refugees,” appealed to the public for “gifts of tobacco.” Even for victims of fire, smoke was then considered a balm. On Black Sunday 1926, Harry King, a young survivor at Worrley’s Mill where fourteen people died, crawled scorched and half-blinded for four kilometres through the smoking forest to tell his story in gasps. At the end of his breathless account, he opened one badly burned eye and whispered: “I’m dying for a smoke, dig.”
The ferocity of “the flume”
The years of the most fatal firestorms were burned into the memories of bush dwellers: 1851, 1898, 1926, 1939, 1967, 1983, 2002–03 and 2009. Stretton’s vivid word-picture of Black Friday 1939, which became a prescribed text in Victorian Matriculation English, joined the paintings by Strutt and Longstaff in forming a lineage of luminous fire art.
The most frightening and fatal firestorms have all roared out of the “fire flume.” That’s what historian Stephen Pyne called the region where hot northerly winds sweep scorching air from the central deserts into the forested ranges of Victoria and Tasmania. In the flume, bushfires strike every year, firestorms every few decades. Firestorms are generated when spot fires ahead of the flaming front coalesce and intensify, even creating their own weather. They entrap and surround. Firestorms are bushfires of a different order of magnitude; they cannot be fought; they rampage and kill. Their timing, however, can be predicted. They come at the end of long droughts, in prolonged heatwaves, on days of high temperatures, low humidity and fierce northerly winds.
The firestorms are intensified by particular species of trees — the mountain ash and the alpine ash — that conspire to create a raging crown fire that kills and then reproduces the whole forest en masse. These tall ash-type eucalypts need a hot, fast-moving crown fire, upon which their regeneration uniquely depends, to crack open their seeds. The ecology of the forest depends on firestorms, so we know they also happened under Aboriginal ecological management.
In the last 200 years, the clearing, burning and intensive logging of the new settlers exaggerated and intensified the existing rhythm. In many remaining forest districts firestorms have come too frequently for the young ash saplings to grow seed, and so towering trees have given way to scrubby bracken and acacia. Those two colonial paintings captured the fatal, colliding elements of the Victorian firestorm: the peril, horror and panic of the people, and the indifferent magnificence of the tall, fire-hungry trees.
In 2009, I resisted use of the word “unprecedented” to describe Black Saturday because it was the familiarity of the firestorm that horrified me. Although the event was probably exacerbated by climate change, the recurrent realities were more haunting. As I wrote in Inside Story at the time, “the 2009 bushfires were 1939 all over again, laced with 1983. The same images, the same stories, the same words and phrases, and the same frightening and awesome natural force that we find so hard to remember and perhaps unconsciously strive to forget.” As a historian of the fire flume, I was disturbed by Black Saturday’s revelation that we had still not come to terms with what we had already experienced.
In the months following Black Saturday (2009), I was invited to assist the small community of Steels Creek in the Yarra Valley to capture stories of their traumatic experience. Working with historians Christine Hansen, Moira Fahy and Peter Stanley, I wrote a history of fire for the community that presented the ubiquity and sheer repetitive predictability of the phenomenon in that valley. One bushfire after another, year in year out. As we set out this rhythm, a deeper pattern emerged, which was the distinction in this region between bushfires and firestorms. The ferocity of the firestorms was generated not necessarily by trees near a settlement but by forests more than ten kilometres away, perhaps thirty or forty kilometres away. Survival in summer is not just a matter of clearing the gutter but also knowing what forests live in your region.
It has proven too tempting and too easy for Australians to overlook or deny the deep local history of the Victorian firestorm. Sometimes Aboriginal mosaic burning, which was applied to so many drier woodlands across the continent, is assumed to have been used in the wet ash forests too. For example, in his book Dark Emu, Bruce Pascoe argued that “a mosaic pattern of low-level burns” was used in mountain ash forests and suggested that wild fires in the forests affected by Black Saturday “were largely unknown before the arrival of Europeans.” But this cannot have been the case, for when Europeans arrived they found mature, even-aged ash forests, the very existence of which was evidence of historical, powerful crown fires.
For example, botanist David Ashton identified one old stand of mountain ash at Wallaby Creek as dating from a firestorm in 1730. Furthermore, ash forests would have been destroyed by frequent fires, and low-level burns are not feasible in such a wet ecosystem. Aboriginal peoples would have used low-level cool burns to manage the drier foothill forests but not the ash forests themselves, for mature mountain ash trees can easily be killed (without germinating seed) by light surface fire. Woiwurrung, Daungwurrung and Gunaikurnai peoples used the tall forests seasonally and probably burned their margins, maintaining clearings and pathways along river flats and ridgetops. They were familiar with the forest’s firestorms and would have foreseen and avoided the dangerous days.
Even six generations after Black Thursday 1851, we stubbornly resist acknowledging the ecological and historical distinctiveness of the Victorian firestorm. It is astonishing that the Black Saturday royal commission cranked through 155 days of testimony but failed to provide a vegetation map in either its interim or final report. In one of my submissions to the inquiry, I drew the commission’s attention to this absence in their interim report, but it was not remedied. Senior counsel Rachel Doyle was more interested in pursuing the former Victorian police chief Christine Nixon about her haircut on 7 February than in directing the commission’s attention to the unusually combustible forests through which the fires stormed.
The royal commission went some way towards being more discriminating about the variety of bushfire, weather, topography and ecology, but not far enough. Forests featured in the commission’s report mostly as “fuel.” “The natural environment,” the commissioners explained in opaque bureaucratic language, “was heavily impacted.”
Thus the firestorm’s origin in the ecology of the forest was ignored even by a royal commission. Or people explained it away by interpreting such outbreaks as entirely new, as products of either the cessation of Aboriginal burning or of anthropogenic climate change. Indigenous fire and global warming are highly significant cultural factors in the making of fire regimes, but both work with the biological imperative. It is clearly hard for humanity to accept the innate power of nature.
The same tendency led Victorians up the garden path of fire policy. The most shocking fact about Black Saturday 2009 was that people died where they thought they were safest, where they were told they would be safest. Of the 173 people killed on Black Saturday, two-thirds of them died in their own homes. Of those, a quarter died sheltering in the bath.
As I wrote in Inside Story in 2009 and 2012, the “Stay or Go” policy was a death sentence in Victorian mountain communities in firestorm weather. Although the policy guided people well in many areas of Australia and had demonstrably saved lives and homes elsewhere, it misled people in this distinctively deadly fire region to believe that they could defend an ordinary home in the face of an atomic force. And it was this confidence in the defensibility of the home and denial of the difference of the firestorm (coupled with a faith in modern firefighting capacity) that underpinned the lack of warnings issued by authorities to local residents about the movement of the fire front on Black Saturday.
For much of the history of these forests, including their long Aboriginal history, no one believed their homes were safe in a firestorm. Evacuation was the norm. Sometimes the elderly and vulnerable were extracted by force from their homes by caring relatives and friends. Most people fled of their own accord. A “safe place” was a creek, a bare or ploughed paddock, a safely prepared or quickly excavated dug-out, a mining adit or railway tunnel, or just somewhere else. If you were trapped at home, there was an art to abandoning it at the right moment. The acknowledged vulnerability of homes made it essential for those caught in them to get out. And people in those earlier times were more inclined to look out the window, go outside and watch the horizon, sniff the air.
In 2009, the internet was a killer. The private, domestic computer screen with its illusion of omniscience and instant communication compounded the vulnerability of the home.
The Black Summer
The fire season of 2019–20 was completely different in character from Black Thursday (1851) and its successors. It might be compared best with the alpine fires of 2002–03, which were also mostly started by lightning in remote terrain and burned for months.
Coming after severe drought and more record heatwaves, the summer of 2019–20 tipped fire patterns into widespread rogue behaviour. It is not unusual for Australians to have smoke in their eyes and lungs over summer — the Great Fires of our history are remembered not only for their death tolls but also for their weeks of smoke and dread. But in the summer of 2019–20 the smoke was worse, more widespread and more enduring, the fires were more extensive and also more intense, NSW fires started behaving more like Victorian ones, and the endless “border fire” symbolically erased the boundary anyway.
Australia was burning from the end of winter to the end of summer, from Queensland to Western Australia, from the Adelaide Hills to East Gippsland, from the NSW south coast to Kangaroo Island, from the Great Western Woodlands to Tasmania. Everywhere, suddenly, bushfire was tipping into something new.
As spring edged into summer and the fires worked their way down the Great Dividing Range and turned the corner into Victoria, people who remembered Ash Wednesday (1983) and Black Saturday (2009) braced themselves. January and February are traditionally the most dangerous months in the southern forests. But this time central Victoria’s good winter rainfall and wetter, cooler February prevented the flume from ripping into full gear.
Therefore an unusual aspect of the fire season of 2019–20 was that these Great Fires did not explode out of the firestorm forests of Victoria and Tasmania. It was one reason why the death toll for such extensive and enduring fires was relatively low; they did not break out in the most fatal forests. Another reason was that Black Saturday had led to a new survival policy: to leave early rather than to stay and defend. Early evacuation thus became the enforced strategy of authorities well beyond the firestorm forests. Again, a regional and ecologically specific strategy became generalised as a universal policy. But at least this time it erred on the side of caution and surely saved lives.
The sheer range, scale, length and enduring ferocity of these fires made them unprecedented. The blackness of the named days of Australia’s fire history describe the aftermath of the sudden, shocking violence of a firestorm; it evokes mourning, grief and the funereal silence of the burned, empty forests. Black and still.
But when the fires burn for months, a single Black Day morphs into a Black Summer. There seemed never to be a black day-after; instead the days, the weeks, the months were relentlessly red. Red and restless. The colour of danger, of ever-lurking flame, of acrid orange smoke and pyrocumuli of peril. The smoke killed ten times more people than the flames. The threat was always there; it was not over until the season itself turned — and only then was it declared black. But the enduring image is of people cowering on beaches in a red-orange glow, awaiting evacuation. I think of it as the Red Summer.
Living with fire
A long historical perspective can help us come to terms with “disasters” and even ameliorate them, but most significantly it can also enable us to see beyond the idea of fire as disaster. There will be more Black Days and, under the influence of climate change, longer Red Summers. We have to accept and plan for them, like drought and flood. We should aim to survive them, even if we can’t hope to prevent or control them. We must acknowledge the role of global climate change in accelerating bushfire and urgently reduce carbon emissions. And we should celebrate, as I think we are already beginning to do, the stimulus that bushfire can give to community and culture.
In the quest for how to live with fire, Indigenous cultural burning philosophies and practices have much to offer all Australians. Sometimes we can even see a fired landscape (of the right intensity and frequency) as beautiful or “clean,” as Aboriginal peoples do. We are slowly learning to respect cultural burning and its capacity to put good fire back into a land that needs fire. But we must go further and actually allow Indigenous fire practitioners to take the lead again.
Victor Steffensen, a Tagalaka descendant from North Queensland, has written a humble and hopeful book, Fire Country (2020), which is as much about negotiating the bureaucratic hierarchies of fire power as it is about fire itself. As his mentor, Tommy George, declared in frustration, “Those bloody national park rangers, they should be learning from us.”
But cultural burning is not the same as prescribed burning. Sensitive controlled burning might, in some ecosystems, render the land safer for habitation, although it has proven difficult to achieve required levels in a warming world. And in a landscape of transformed ecologies, greatly increased population and rapidly changing climate, it is unreasonable and dangerous to expect Indigenous peoples to make the land safe for the proliferating newcomers; it would again set vulnerable people up to fail. Anthropologist Tim Neale has argued that the settler “dream of control” places an “impossible burden” on Aboriginal peoples, trapping them again within an idealised expectation of unchanging ancient behaviour.
Renewing and reviving Indigenous fire practices is important, first and foremost, for human rights, native title and the health, wellbeing and self-esteem of First Nations communities. We are fortunate that an additional opportunity presents itself: for a rapprochement between the exercise of Indigenous responsibility to Country and modern Australia’s need for labour-intensive and ecologically sensitive fire management on the ground. There is much creative promise in that partnership, and developing it will take time, patience and respect.
Throughout 2019, fire experts pleaded with the federal government to hold a bushfire summit to prepare for the dreaded summer, but the prime minister refused, fearing that acknowledging the crisis would give credence to climate action. Yet at the end of the summer he established another retrospective bushfire inquiry, the fifty-eighth since 1939. Many of the sensible, urgent recommendations of those earlier commissions have been ignored and await enactment. Rather than spending millions of dollars on lawyers after the flames, the nation would do better to spend a few thousand on environmental historians to distil and interpret existing, hard-earned wisdom.
Australian scholars of fire need to work on at least three temporal scales. First, there is the deep-time environmental and cultural history of the continent and its management over millennia. Second, there is the century-scale history of invasion, documenting the changes wrought by the collision of a naive fire people with the fire continent. And third, there is the long future of climate-changed nature and society. Black Thursday was the first firestorm after the invasion, an ancient ecological cycle with new social dimensions. Red Tuesday, Black Sunday and Black Friday were exaggerated by settlement and rampant exploitation. Black Saturday was more like the past than the future, a frighteningly familiar and fatal amalgam of nature and culture. But the Red Summer of 2019–20 was a scary shift to something new, fast-forwarding Australians into a new Fire Age. •
This is an abridged version of “The Fires: A Long Historical Perspective,” Tom Griffiths’s contribution to The Fires Next Time: Understanding Australia’s Black Summer, edited by Peter Christoff (Melbourne University Publishing, 2023).